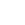Chronic UTIs are resistant to treatment and can keep coming back despite undergoing treatment. If you have UTI relapses several times after treatment you are likely to be diagnosed with chronic urinary tract infection.
Symptoms of Chronic UTI
If you have chronic UTI you are already familiar with the symptoms of UTI. These symptoms persist when you have chronic UTI.
- dark or cloudy urine
- frequent urination
- burning sensation while expelling urine
- your lower back or abdominal pain
- nausea and vomiting
- chills and fever
- mental confusion
Types of Chronic UTIs
 Bladder Infections (or cystitis)
Bladder Infections (or cystitis)
The source of bladder infections is usually the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli) which is found naturally in the intestines but becomes dangerous when it finds its way into the urinary tract. This can occur when toilet water splashes on your genital area, during sexual intercourse, anal sex, or because of poor cleaning habits.
Urethral Infections (or urethritis)
Urethritis can also be caused by E. coli although it is mainly sexually transmitted and occurs with STI infections like gonorrhea, herpes or chlamydia. These usually attack the urethra and rarely cause infections of the bladder.
Who is at risk of chronic UTI?
The woman’s anatomical structure makes her more likely to get chronic UTI because of the short urethra which is close to the rectum. You must wipe front to back so that e-coli does not get into contact with urethra because even microscopic fecal matter can result in UTI.
Using diaphragms during sex pushes against the urethra and blocks the ability to empty bladder completely thus increasing your chances of chronic UTI.
If you often use antibacterial soaps, antibiotics or chemical products which change your vagina’s bacterial composition you are increasing the risk of developing chronic UTI. For the same reason, the hormonal changes during menopause can lead to chronic UTIs.
Diagnosis and Treatment of chronic UTI
 If you have chronic UTI it implies that you have been diagnosed with UTI before and there could be many reasons for the recurring problem. In addition to examining your urine sample, your doctor may scan your body using imaging equipment to examine your urinal system for kidney damage or, may use cystoscopy, where a long thin tube with lenses is put through your urethra to your bladder. Normal UTIs are treated within a week with antibiotics and pain medication but chronic UTI necessitates a long term dose to help treat and prevent the relapse of symptoms. Your doctor could recommend taking antibiotics daily and after having sex. To monitor your urinary system closely you can perform home tests and report to your doctor the progress. When chronic UTI is caused by menopause you may consider therapy that gives estrogen therapy for your vagina.
If you have chronic UTI it implies that you have been diagnosed with UTI before and there could be many reasons for the recurring problem. In addition to examining your urine sample, your doctor may scan your body using imaging equipment to examine your urinal system for kidney damage or, may use cystoscopy, where a long thin tube with lenses is put through your urethra to your bladder. Normal UTIs are treated within a week with antibiotics and pain medication but chronic UTI necessitates a long term dose to help treat and prevent the relapse of symptoms. Your doctor could recommend taking antibiotics daily and after having sex. To monitor your urinary system closely you can perform home tests and report to your doctor the progress. When chronic UTI is caused by menopause you may consider therapy that gives estrogen therapy for your vagina.
To prevent recurring UTIs, you should maintain good hygiene, urinate when you feel the urge, wear cotton underwear and drink a lot of water daily to get rid of bacteria.
Chronic UTI increases your risk of kidney diseases, kidney damage, sepsis, septicemia (when bacteria gets into the blood stream) and the risk of preterm births or low birth weight. Seek treatment when you experience symptoms of distress that could be a possible UTI problem to reduce the chances of chronic infection.