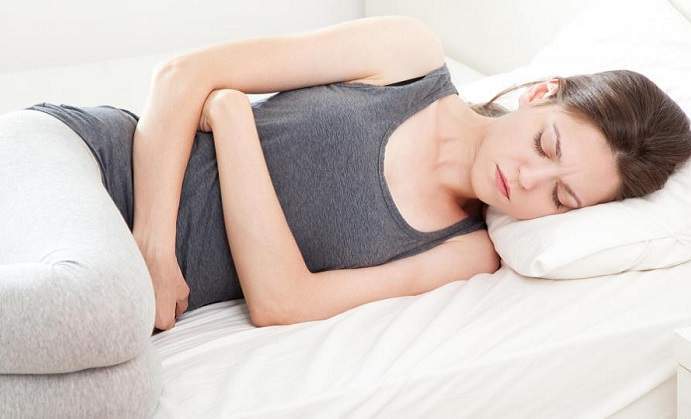
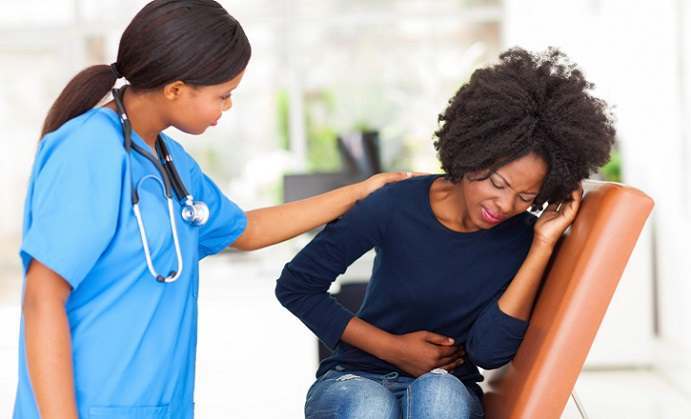
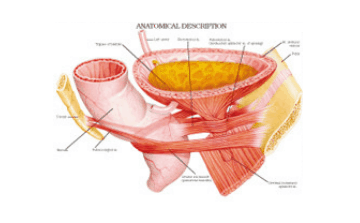
A UTI or Urinary Tract Infection is due to bacteria that get inside your urinary tract. Most bacteria that enter your urinary tract are expelled when you urinate. If the bacteria stay in your urinary tract, you may get an infection. Your urinary tract includes bladder, urethra, kidneys and ureters. Urine is made in your kidneys, and it flows from the ureters to the bladder. The bladder helps in dispelling the urine from the body. It is the lower urinary tract, which includes your bladder and urethra that a urinary tract infection is most commonly found.
Common UTI symptoms include:
- A constant urge to urinate
- Releasing only small amounts of urine at a time
- Bloody, cloudy, or bad-smelling urine
- Abdominal or lower back pain
- Burning pain during urination
 A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria (or, less commonly, a virus or even a fungus) enters the urinary tract. Whether the infection affects a man or a woman, the treatment is the same: a round of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and get rid of UTI symptoms.
A urinary tract infection occurs when bacteria (or, less commonly, a virus or even a fungus) enters the urinary tract. Whether the infection affects a man or a woman, the treatment is the same: a round of antibiotics to kill the bacteria and get rid of UTI symptoms.
But there are also things men can do to help prevent a UTI from setting in — especially if they have any of the risk factors. If you’re a man, take these steps to reduce your risk of getting a UTI:
- If you’re not circumcised, thoroughly clean the area beneath the foreskin each time you shower.
- Drink lots of fluids — water is best — every day.
- Don’t hold your urine — make frequent trips to the bathroom.
- Carefully cleanse your genitals before and after sex to help get rid of bacteria (this will also help your partner avoid UTIs).
- Wear condoms when you have sex.
A doctor will ask about your signs and symptoms. He may press on your stomach, sides, and back to check if you feel pain. You may also need the following tests:
 Urine tests: A sample of your urine is collected and sent to a lab for tests to learn what germ is causing your infection. By urinating into a cup, one can give a sample of the urine.
Urine tests: A sample of your urine is collected and sent to a lab for tests to learn what germ is causing your infection. By urinating into a cup, one can give a sample of the urine.
Blood tests: You may need blood tests to check if you have a prostate infection.
Imaging tests: You may need imaging tests if your UTI does not get better or you get another UTI. Imaging tests are pictures of your urinary tract that may show if your infection is in your kidneys. Imaging tests may also show if you have damage, blockages, or other problems in your urinary tract.
You may be given a dye before the pictures are taken to help caregivers see the pictures better. Tell the caregiver if you have ever had an allergic reaction to contrast dye.
The infection is treated through antibiotics.
One can prevent the occurrence of UTIs by following certain steps:
- Urinate when you feel the urge: Do not hold your urine. Urinate as soon as you feel you have to.
- Drink plenty of liquids: This may help you urinate more often. Ask how much liquid you should drink each day and which liquids are right for you.