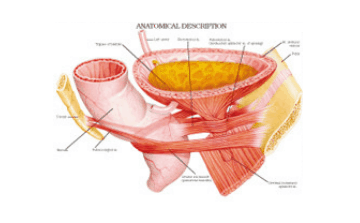
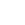Your urinary tract is made up of the kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra. Urinary Tract Infections can affect any of these parts if bacteria get inside them. The bacterium Escherichia coli (E.coli) can be passed from the rectal area is the cause of most UTIs. Bladder infections are the most prevalent type of UTI such that the names UTI and Bladder Infection are usually used interchangeably.
Types of UTI
 Urinary tract infections are classified into 2 major types basing on the location of the infection.
Urinary tract infections are classified into 2 major types basing on the location of the infection.
The Lower Tract Infection
It affects the urethra (urethritis) and the bladder (cystitis).
The Upper Tract infection
It affects the kidneys and is also known as pyelonephritis. Bacteria can enter the kidneys from the bloodstream or from an infected bladder.
Pyelonephritis is a very fatal condition, for that reason UTI should be treated as soon as they are discovered while still at the urethra or bladder.
The risk factors of UTI
These factors make certain people more susceptible to being infected with UTI.
- Pregnancy
- Short urethra that is near the rectum (women)
- Unprotected sex
- Stress
- Weak immune system because of illnesses like diabetes or HIV
- Poor hygiene
- Enlarged prostrate
- Defects of the urinary tract
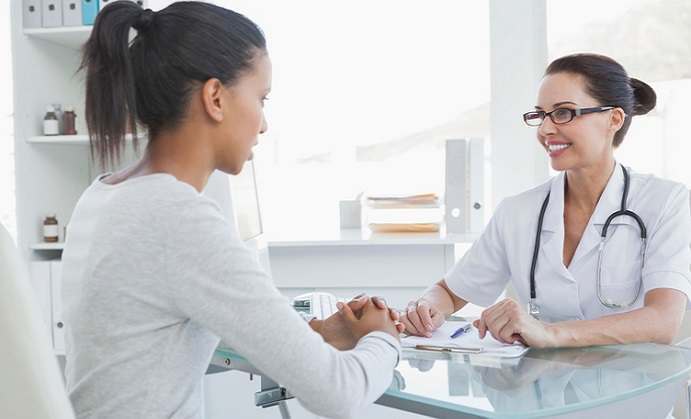
Diagnosing and Treating UTIs
 UTIs are diagnosed by analyzing your urine sample to find out whether there are bacteria in it (urinalysis) and which type of bacteria they are (urine culture) so that the best treatment can be determined. The presence of blood in the sample also indicates that you have UTI. In some cases diagnosis might entail observing you via imaging devices like ultrasound scan. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics to restore the state of your urinary tract by getting rid of the bacteria which is causing the infection.
UTIs are diagnosed by analyzing your urine sample to find out whether there are bacteria in it (urinalysis) and which type of bacteria they are (urine culture) so that the best treatment can be determined. The presence of blood in the sample also indicates that you have UTI. In some cases diagnosis might entail observing you via imaging devices like ultrasound scan. The doctor will prescribe antibiotics to restore the state of your urinary tract by getting rid of the bacteria which is causing the infection.
Your doctor will suggest that you take painkillers or anti-inflammatories to reduce pain and discomfort caused by the infection. The infection and its symptoms will clear within a few days. Antibiotics have side effects like weakening your immune system, risk of yeast infection or recurrent UTI. Alternatively, you can opt for natural remedies such as drinking water, cranberry juice or dietary supplements.
Taking Care of Your Urinary Tract to Prevent UTI
You can prevent the possibility of becoming infected with UTI by taking care of your urinary tract and maintaining good personal hygiene. There are several ways of minimizing the entrance of harmful bacteria into your urinary system.
The do’s
- Drink water and other fluids daily
- Wipe from front to back after passing waste
- Wear absorbent cotton underwear
- Wear loose-fitting clothes
- Change sanitary pads or tampons frequently
- Urinate and/or bathe after sexual intercourse to remove bacteria from your urethra
- Use contraceptives which do not have contaminants
- Wash the genital area with mild soap and water
The don’ts
- Don’t use harsh products like sprays when washing the genital region
- Don’t procrastinate urination whenever your bladder signals
- Don’t take too much of acidic, caffeinated or carbonated food or beverages